Hello,
We all aware that Oracle Automatic storage management offers striping of disks but propreitory of its own method.
To stripe data, Oracle ASM separates files into stripes and spreads data evenly across all of the disks in a disk group. It has two methods of striping, Fine & Coarse.
Fine Striping:- Fine striping writes 128 KB data to each ASM Disk in the diskgroup in a round robin fashion, 128 KB goes to the first disk, then the next 128 KB, goes to the next disk, etc. According to manual, The fine-grained stripe size always equals 128 KB in any configuration; this provides lower I/O latency for small I/O operations.” Small I/O operations sure sounds like a good candidate for redo logs, control files etc.
Coarse Striping:-With coarse grained striping ASM writes data to each disk in the same round robin fashion, but writes chunks in the size of the ASM instance’s allocation unit (AU) size, default is 1MB.
Further, starting from 11gR2, Online redo log files are no more in Fine striping contradictory to 10g, as Oracle silently changed the template to Coarse striping.
A note has been written on the same:- Redo Log Striping In 11.2 ASM, is Coarse Or Fine? [ID 1269158.1]
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
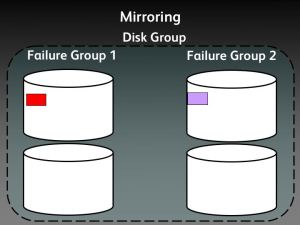
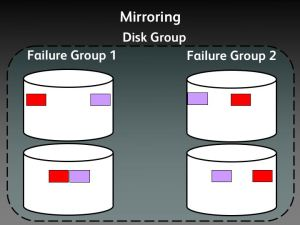
Mirroring
ASM mirroring has three types, External, Normal, High
External:- No mirroring from Automatic storagement
Normal:- Two Way mirroring, (Required two diskgroups)
High:- Three way mirroring, (Required three diskgroups)
Mirroring as you aware the copy of same extents to multiple disks
Further along with mirroring, Oracle Intelligently place the extents in two modes,
COLD, MIRRORCOLD - use the inner most tracks (closest to spindle) on the disk drive.
HOT, MIRRORHOT - Use the outermost tracks which have greater speed and higher bandwidth.
Please look at the diagrams explaining about Striping.
Please look at the diagrams explaining the mirroring
-Thanks
Geek DBA


Follow Me!!!