Welcome to first Post on MongoDB.
Given my experience over RDBMS during past decade, exploring the current NOSQL database technologies and keep ourself updated. This will not only help ourselves but also enable us to know where to use this, since majority NOSQL databases are not fit for everything, they are customised and fit for purpose, Like MongoDB have this issues.
- cannot be used for transactional purpose or commerce/erp applications since its cannot meet the ACID requirements (partial available).
- MongoDB states that complex queries / joins / aggregations should be avoidable as much as possible.
- The more the normalized data it suit good but it inherits duplicacy in data.
- Familiar SQL language is not useful, you should know how to write a query with complex {,}() etc.
- Schemaless , means not a defined characteristic, means anyone can with any type of data is loaded, means if application required an specific characteristics like datatype check etc.
- As version evolves, the changes to the database core engine, there is subtle difference between 2.0, 2.6 and 3.2, much more changes and one to keep understand all those.
- More relies on OS Page cache and flush mechanism no control over but can ask OS to flush often
- Cannot call as a Fully High Availability Database, hence the new definition BASE, (Basic Availability + Eventual Consistency)
- Basic Availability - At one point of time, if you loose a shard (with all replica sets) until that shard is available , data is not availabel to business
- Eventual Consistency - No guarantee that data is shown was consistency, typical example (Thanks to Tim Hall) - Inventory stock in webcommerce can show in two different sessions although the order for that stock is already placed. You will get refund for your order or your order get cancelled after a while
- Locking - As version changes MongoDB locks also got changed drasitically, initially a database level lock, then a collection level as of 3.2 Document Level lock
- Locking - Readers lock the writer (shared lock) as of old version
- MVCC - No undo, until 3.2 , unless use wiredtiger engine
- Storage - Double sizing due write ahead allocation.
The above is small set of what I understand from small implementations and reading documents. The following is the list of common keywords that we know as Oracle DBA's and what they called in MongoDB.
| Oracle | MongoDB | Description |
| SGA | No SGA | MongoDB relies completely on OS Page Cache and Flushing Mechanisms, No Specific SGA concept |
| BufferPool | OS Level Page Cache | Controls by OS |
| Shared Pool | Query Cache | MongoDB Manages all statements parsed by three query frameworks Query,Aggregation,Sort and the query passes through this engines and parse control by "internalquerycachesize" parameter |
| Dictionary | loaded into memory through .ns file | Stores in memory map in the physical ram and use OS level mmap, while mongodb starts this metadata is loaded into memory and map the physical structures through the namespace file |
| spfile/pfile | /etc/mongod.conf | Contains data directory location etc. Port, Sharding, Replication, security informations |
| StorageEngine | mmapv1
wiredtiger inmemory |
This is what I look this is adopted by MySQL terminology MYISAM , INNODB, The Memory Storage Engine
Similarly until MongoDB 3.0 uses default mmapv1, and 3.2 allows wiredtiger as default engine basically (uses read/write or MVCC) and the final one is memory engine |
| Database Server | mongod | mongod is database instance |
| Database Client | mongo | Like SQLPLUS Shell |
| Database Listener | Router aka mongos | In a sharded cluster the mongos instance receives all connections and process |
| Dictionary | Config Servers - mongod | MongoD instances roles can be Database, configserver, sharded database |
| redolog | journalfile | A file called .j_0 is created in journal folder under storage directory and any write operations writes data to this file before flush for durability purposes, journal file is used for recovery purposes. Once the journal entry is written even mongod crashed without flushing dirty buffers to disk, this journal helps to reapply the statement, well like our instance recovery |
| database | database | A database is associated with a namespace file at physical level with default 16MB size and can contain 12000 collections means 12000 tables, and the filename like dbname.ns , which typically contains collections names and indexes details and this file will be mapped in memory |
| schema | None | |
| datafile | datafile | datafile denotes with database name for example if my database is mydb1 then datafile looks like mydb.1 , mydb.2 etc. Each file starts with 64MB and new file created doubling the size, So as your database grows the files grows. |
| alertlog | /var/log/mongodb/mongod.log | Log for mongodb |
| Datatypes | See table other side | |
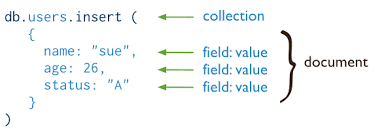
| table | collection | A table is a collection associated with .ns file which loaded into memory |
| row | document | |
| Joins | embedded documents or linking | |
| shutdown | use admin; db.shutdownServer() | |
| startup | service mongod start | |
| expdp | mongodump --out <directory> | |
| impdp | mongorestore <directory> | |
| v$sysstat | db.stats() | |
| v$lock | db.currentOp() | shows locks information as well current operations in that node. |
| v$session | db.currentOp() | |
| kill session | db.killOp(opid) | |
| v$osstat | db.serverStatus() | |
| dba_tables | db.collection.stats() | |
| Create Table | implicit creation | When you insert a first row, the table is implicitly created, no definition is required
|
| Drop Table | db.tablename.drop() | |
| Add column | db.collection.update( set) | To add a column db.users.update( { }, { $set: { join_date: new Date() } }, { multi: true } ) |
| Drop Column | db.collection.update( unset) | db.users.update( { }, { $unset: { join_date: "" } }, { multi: true } ) |
| select | db.tablename.find() | |
| select only few columns | See other column | db.users.find( { status: "A" }, { user_id: 1, status: 1, _id: 0 } ) |
| select with where | see other column | db.users.find( { status: "A" } ) |
| insert | Insert will eventually create a table | db.users.insert( { user_id: "bcd001", age: 45, status: "A" } ) |
| update | Update a column age > 25 with status C | db.users.update( { age: { $gt: 25 } }, { $set: { status: "C" } }, { multi: true } ) |
| delete | db.tablename.remove() | |
| select with join | as of 3.2 version you can use $lookup | |
| Group by | db.tablename.group() | only available in 3.2 , earlier versions should use db.tablenameaggregate(). |
| count | db.tablename.count() | Count the documents i.e rows |
| OEM | MMS | GUI tool |
| RAC | Sharding | MongoDB use sharded cluster, each node will have its own partition of data through the key (range,hash,tag) |
| ASM | Nothing like that | Uses OS Filesystem page cache |
| Diskgroups | Disks | Uses disks |
| ASM Mirroring | Replica Sets | |
| Clustering | Sharding with ReplicaSets | Manage BASIC Availability, in event of a node failure with replica sets the data is partially available not completely hence called BASIC Availability not high availability |
| Private Network | No need of private network | |
| addnode | sh.addShard("localhost:portnum") | |
| Listener | Router or MongoS | in a cluster environment to redirect to specific shard for your query, the mongos instance will be used, |
| Client | Mongos | mongos is the instance that run client like tns entry |
| Nothing like that | Configservers | ConfigServers contains information about data distribution keys and route the request to certain shard. It synchronises the metadata often. |
| Master-Slave | Master-Master | MongoDB maintains a router instance called mongos and connect |
| redolog threads | oplog | In rac we use threads to detect the instance specific actions, here in MongoDB the high availability means at node level which contain the Primary and replica set with in the node itself, so the Primary and replica set maintain polling mechanism, to ensure all changes replicated to the replica set Oplog will be used for that node only. |
| datafile resize | db.repairDatabase() | Reduces the Datafiles for that databases |
| create user | db.addUser | db.addUser({ user: "geek", pwd: "password", roles: [ "readWrite", "dbAdmin" ] }) |
| dba_users | db.system.users.find() | |
| create database | use dbname | Eventually Create a new database. |
| drop database | db.dropDatabase() | |
| v$banner | db.version() | |
| voting | heartbeat voting between replicatset | uses arbiter process to vote between a primary and secondary replica set in two node replicaset, remember not the other shards. |
| Optimizer | plancache | Plan cache is a program that resides in the memory and process the query |
| Statistics | Maintain metadata in the extents | Like the datafile header in oracle contains the extent information the table statistics is maintain in extents in the ns file |
| listener | router aka mongos | Mongos instance works like a listener listen your request, read that request, get the distribution keys from config servers and send request to the nodes. |
| Port 1521 | Port 27017 | Default port is 27017 |
| sqlplus | mongo | mongo shell |
| sql tracing | db.setProfilingLevel(level, slowms) |
|
| cluster status | sh.status() | |
| disk replication status | rs.status()
rs.printslavereplicationinfo() |
Shows how much lag replication is behind primary |
| Disk Striping | sh.enableSharding("students") | in ASM striping is done by default to diskgroups, where in mongodb the striping can be enabled at database level and then at collection level striping what is the basis of striping like which column
sh.shardCollection("students.testData", { "x": "hashed", "_id": "hashed" }) |
| startup | mongod -f <config filename> | mongod is the instance that starts and acts as database node |
| Limits | See the other column | Heaps of limitations and varies with versions See, references, https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/reference/limits/
|
| Flush SQL ID | db.runCommand(
{ planClearCache: "orders" }) |
|
| Explain plan | db.tablename.find(query).explain | You can also explain by query and specific where condition see documentation |
Next Post is on Installing & Creating Standalone MongoDB Database
-Thanks
Geek DBA
Super Comparison document. Kudos to the writer.. Keep good work on. very useful for beginner.