Assuming you have completed docker installation on windows and registered with oracle container registry, Read first part here if not yet done
This post explain how to create a container for mysql and also show some example of managing container etc. In less than 10 mins mysql database is ready and you can practice what ever you like.
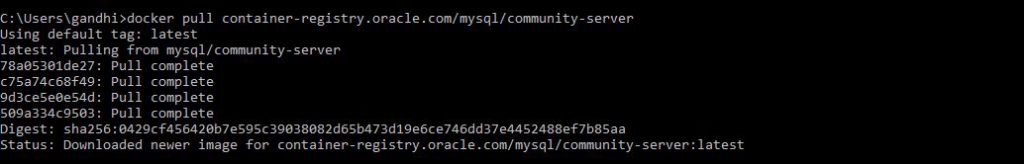
Pull Docker Image and Run the docker with default options
docker pull container-registry.oracle.com/mysql/community-server
Run the docker with mysql image, I have kept the root password and name of docker is mysql5.7
docker run --name mysql5.7 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=sayit -d container-registry.oracle.com/mysql/community-server:lates
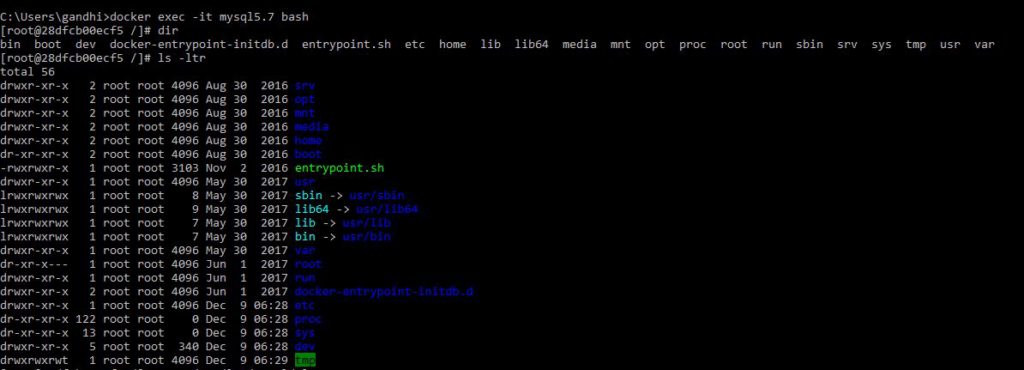
Login to Shell
docker exec -it mysql5.7 bash
Getting connected outside from the docker use -p or -P option while run the docker command
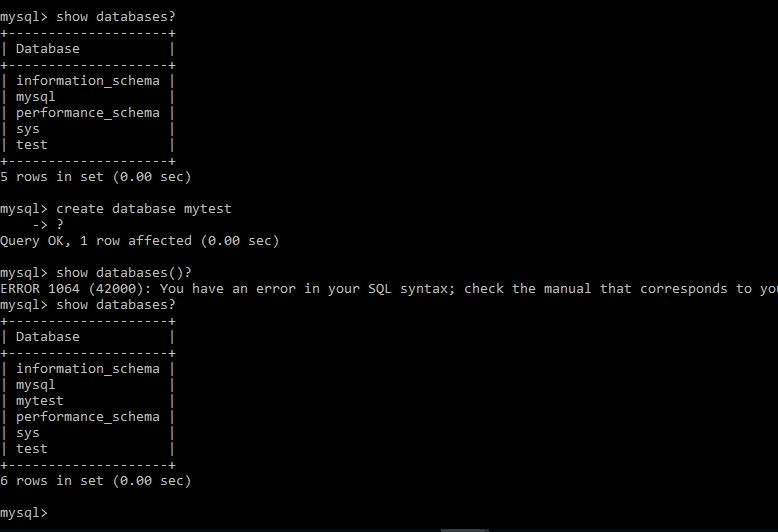
Once logged in , show databases and create databases etc and rest of things will be as usual.
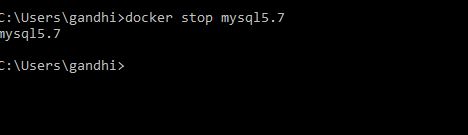
Stop docker container
docker stop mysql5.7
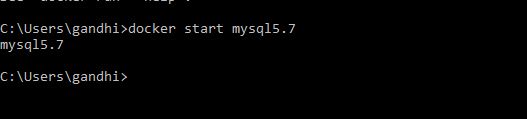
Start docker container
docker start mysql5.7
Remove docker container, you can use -f option to forcefully delete the running docker
docker rm mysql5.6 -f
Further, if you want to keep any additional parameter you can use a cnf file and run the docker run command, this file will replace the cnf file in the docker container 🙂
The MySQL startup configuration in these Docker images is specified in the file /etc/my.cnf. If you want to customize this configuration for your own purposes, you can create your alternative configuration file in a directory on the host machine and then mount this file in the appropriate location inside the MySQL container, effectively replacing the standard configuration file.
If you want to base your changes on the standard configuration file, start your MySQL container in the standard way described above, then do:
docker exec -it my-container-name cat /etc/my.cnf > /my/custom/config-file
… where ´/my/custom/config-file´ is the path and name of the new configuration file. Then start a new MySQL container like this:
docker run --name my-new-container-name -v /my/custom/config-file:/etc/my.cnf -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=my-secret-pw -d container-registry.oracle.com/mysql/community-server:tag
Follow Me!!!