In Oracle (infact for any RDBMS) , will have a memory structures and processes (or thread) to process the data.
If we take Oracle as an example, lets look the similarities
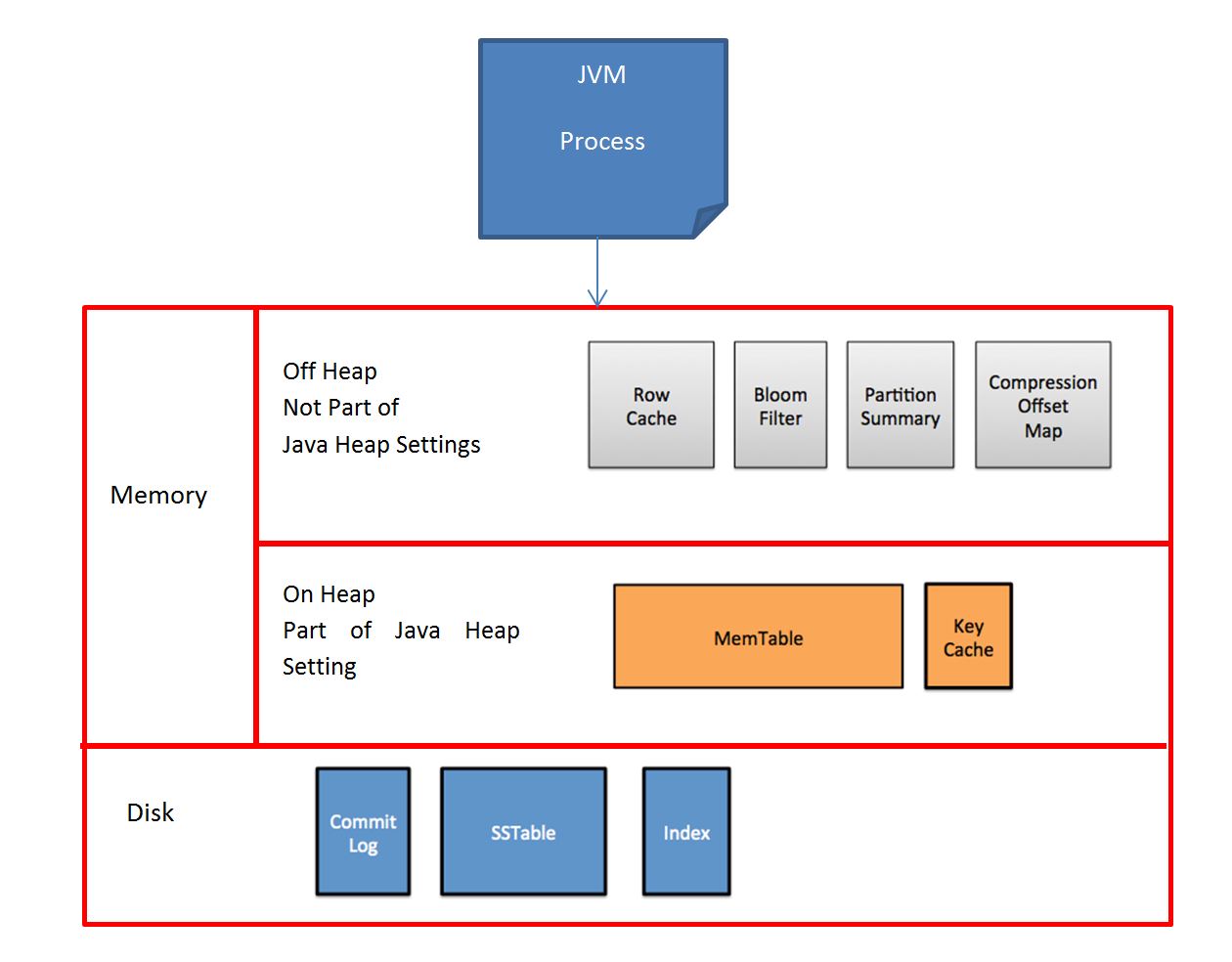
1. Memory Architecture
| Oracle | Cassandra (NO-SQL DB) | Parameter to Set in Cassandra.yaml file | Comments |
| SGA | Java Heap Memory |
cassandraenv.sh MAX_HEAP_SIZE |
SGA is shared global area , where in the Java Heap Memory is used for Cassandra Core Engine |
| BufferPool | Memtables | memtable_total_space_in_mb |
Memtables in Cassandra used for each single table to store the recently used or modifying data, unlike a large buffer cache suppose you have DML on 4 tables , it will create 4 Memtables in the memory |
| Result Cache | Row Cache | row_cache_size_in_mb | As like result cache in Oracle, you can store certain rows (entire rows) in table in memory by using rowcache |
| RowCache | Partition Key Cache | key_cache_size_in_mb |
When an operation has to perform on a block, one must know the Block location in terms of Block Number, Disk number, node name etc. To achieve this, Oracle relies on Data Dictionary Cache and get block number and file number and then read from the disk. In Cassandra, Data Stores on disk based on Partition Key Value and this Key will be stored in Partition Key Cache to effectively get the data from disk |
| Hash Buckets | Bloom Filter | bloom_filter_fp_chance |
In Oracle to find the data block in buffer cache, Oracle uses mod function to find the right bucket for the data. This will help process not to traverse entire block chain. Similarly, Cassandra checks the Bloom filter to discover which SSTables are likely to have the request partition data. The Bloom filter is stored in off-heap memory. Each SSTable has a Bloom filter associated with it. Create table ..... (bloom_filter_fp_chance = 0.01) |
| NA | PartitionSummary |
min_index_interval 128 and max_index_interval 2048, or index_interval 128 |
The partition summary is an off-heap in-memory structure that stores a sampling of the partition index. A partition index contains all partition keys, whereas a partition summary samples every X keys, and maps the location of every Xth key's location in the index file. For example, if the partition summary is set to sample every 20 keys, it will store the location of the first key as the beginning of the SSTable file, the 20th key and its location in the file, and so on. |
| NA | CompressionOffsets |
Compression offset maps holds the offset information for compressed blocks. By default all tables in Cassandra are compressed and more the compression ratio larger the compression offset table. |
2. Physical Structures
| Oracle | Cassandra | Parameter | Comments |
| RedoLog | CommitLog |
commitlog_total_space_in_mb commitlog_segment_size_in_mb |
To maintain the durability of the Transaction any database should write the transaction to off a file like redo log or transaction log or a commit log in case of cassandra. . The purpose of the commitlog is to be able to recreate the memtable after a node crashes or gets rebooted. This is important, since the memtable only gets flushed to disk when it's 'full' |
| Datafile | SSTables |
sstable_size_in_mb sstable_min_threshold |
In oracle the table is stored in form of segments and extents and blocks in a physical datafile. And it is contiguous or non-contigous and fits into a single or multiple large datafiles.
Where the SSTables
SSTables consists of different types:-
|
General Architecture
How Read Occurs in Cassandra?

- Check the memtable
- Check row cache, if enabled
- Checks Bloom filter
- Checks partition key cache, if enabled
- Goes directly to the compression offset map if a partition key is found in the partition key cache, or checks the partition summary if not
If the partition summary is checked, then the partition index is accessed
- Locates the data on disk using the compression offset map
- Fetches the data from the SSTable on disk

How Write Occurs in Cassandra

Cassandra processes data at several stages on the write path, starting with the immediate logging of a write and ending in compaction:
- Logging data in the commit log
- Writing data to the memtable
- Flushing data from the memtable
- Storing data on disk in SSTables
- Compaction, by merging the SSTables

3. Logical Structures
| Oracle | Cassandra | Command | Comments |
| Schema | Keyspace |
CREATE KEYSPACE TEST
WITH REPLICATION = { 'class' : 'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor' : n };
|
Keyspace is a schema a collection of Tables a top level namespace Replication Factor is used to determine the Mirroring of data in a multinode environment |
| Table | ColumnFamily |
CREATE TABLE TEST.Users( ID text, firstname text, lastname text, PRIMARY KEY (ID) ) |
A table is often called as ColumnFamily in NO-SQL , created with primary key , |
| ParitionKey | PartitionKey |
CREATE TABLE TEST.Users( ID text, firstname text, lastname text, PRIMARY KEY (ID) ) |
primary key means the partition key to store the data in column pair not the primary key in Oracle. As like Oracle's Composite Primary Key aka Partitioning you can set multiple columns to the Primary Key |
| Indexes | Index |
CREATE INDEX user_state ON TEST.Users (lastname); |
Creating a simple index whichi inturn creates a file on disk. |
| Sequence | Counter |
CREATE TABLE TEST.page_view_counts (counter_value counter, url_name varchar, page_name varchar, PRIMARY KEY (url_name, page_name) ); |
Here the datatype counter depicts , its a sequence based value, so you just can increment in your dml and code ex: UPDATE counterks.page_view_counts SET counter_value = counter_value + 1 WHERE url_name='www.datastax.com' AND page_name='home'; |
| Trigger | Trigger |
CREATE TRIGGER TEST.myTrigger ON myTable USING 'org.apache.cassandra.triggers.INDEXCHECK' |
In RDBMS, Triggers are stored as compiled code in the memory of the Database called SharedPool/Library Cache, where in the cassandra implementation, To create a trigger, you must first build a jar with a class implementing the ITrigger interface and put it into the triggers directory on every node, then perform a CQL3 CREATE TRIGGER request to tie your trigger to a Cassandra table (or several tables) |
| Type | Type |
CREATE TYPE TEST.address ( street text, city text, zip_code int, phones set<text> ) |
Facilitates handling multiple fields of related information, such as address information: street, city, and postal code. |
| Undo | Tombstones | gc_grace_seconds | Deletes do not remove the rows and columns immediately and in-place. Instead, Cassandra writes a special marker, called a tombstone, indicating that a row, column, or range of columns was deleted. These tombstones are kept for at least the period of time defined by the gc_grace_seconds per-table setting |
Image Courtesy: Datastax
-Thanks
GeekDBA
Follow Me!!!