I will start this post with a Grid Infrastructure installation slide, which ask you the type of cluster you want to install.

As you noted, "Standard Cluster" and "Flex Cluster". We understood by now standard cluster is a traditional cluster. Now let's explore what is Flexcluster is.
Generally, an application layer and a database layer can be together and managed by a single cluster. So every node in cluster should have an access to the shared storage i.e Voting disk and OCR and every node should be tightly connected with shared storage. This tightly coupling will lead to the contention in the storage i.e voting disk polling by every node and also can cause cluster interconnect contention i.e network heart beat ping to all nodes need to be done. Another issue is that scalability, since the cluster can be limited to 100 nodes this can be a greater problem for larger enterprise system. Since both Application and Database layers may need to be managed as a single cluster so that entire services can be managed with high availability infrastructure.
Actually the application layer nodes need not to have access to shared storages, indeed the database layer since the data and the criticality lies here. To overcome this,
From 12c onwards, Flexcluster is designed over HUB-LEAF topology to scale the Cluster to large number of nodes, literally 1000s of nodes. Hub nodes are very much similar to the standard cluster architecture, they are tightly coupled through a private interconnect and have direct access to shared storage. On the contrary, Leaf nodes are very light weight servers, not connected to other leaf nodes, and have no direct access to the storage. A Hub node can have multiple leaf nodes, but, a node leaf can’t be part of multiple of Hub nodes. In a nutshell, the prime purpose of an Oracle Flex Cluster is to provide the combined database and application tiers together in a single clustering environment.
From Gridinfrastructure perspective, the hub nodes are database nodes contains full blown GI stack, where the Leaf nodes are typically application (middle layer) contains smaller footprint of GI stack.
Take an example of 12 node (3 DB, 9 Application nodes) if connected to a standard and flex cluster.
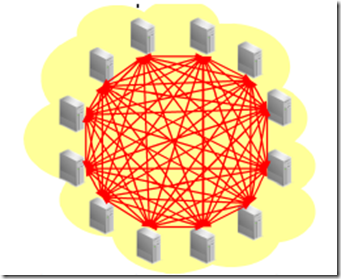
In standard cluster environment below, all nodes connected to each other and accessed the shared storage, see the cluster interconnect contention
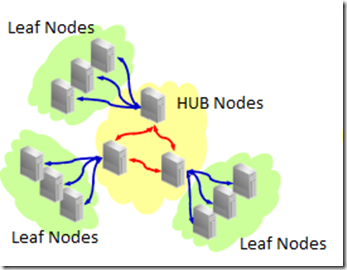
In below diagram, with 12c FlexCluster the app nodes refer to as leaf nodes and the center ones are db nodes called hub nodes.
Here the leaf nodes (typically services/module) of application connected to the nodes to the db service. so each group of Leaf nodes will connect to one db node,
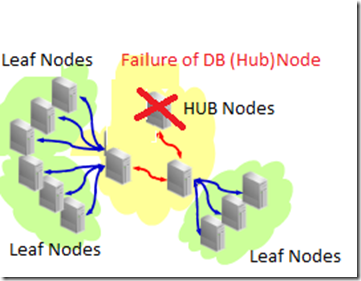
when a db node i.e hub node fails the db service failed over to other db nodes, then the leaf nodes attached to that hub node also failed over to another hub node where the service is running. See diagram below.
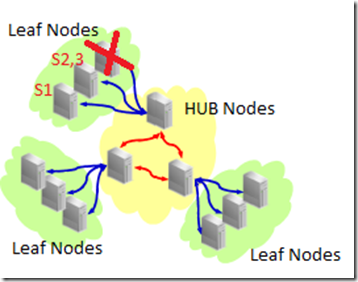
But when a leaf node is failed, the services attached to this leaf node will be failed over to another leaf node.
Image sources: Internet (modified a bit)
So this is the concept of Flex Cluster, BTW do not confuse with FlexASM both were different concepts.
Enabling Flexcluster ....
Happy reading.....
-Thanks
Geek DBA
Follow Me!!!